1.9 Connections
Wirings between Transformer inputs and outputs.
Diagram 1.0: The Transformer, Vaswani et al. (2017)
An initial glimpse of the Transformer may raise questions regarding why both encoder and decoder have inputs. This is not made entirely clear in the original Vaswani et al. (2017) paper. The following diagrams depict why - the decoder blocks take as input the encoded initial input sequence, as well as the generated tokens that the Transformer itself has generated, and continue to feed newly generated tokens back into the decoder until the output sequence is finished.
Note also that Transformers are typically stacked, and the logic behind this is akin to adding more layers to a neural network; it is .
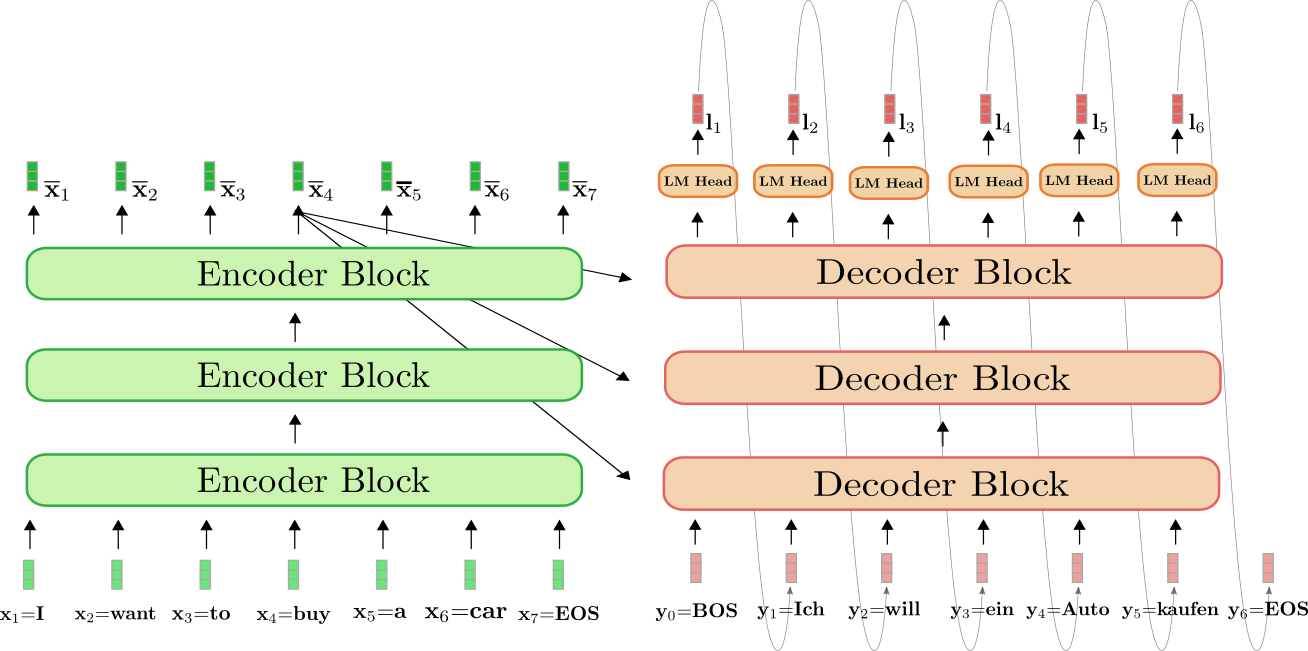 Diagram 1.8.1: an LLM performing a machine translation task, note that this model features stacked encoders and decoders, not uncommonly. Source: HuggingFace blog
Diagram 1.8.1: an LLM performing a machine translation task, note that this model features stacked encoders and decoders, not uncommonly. Source: HuggingFace blog
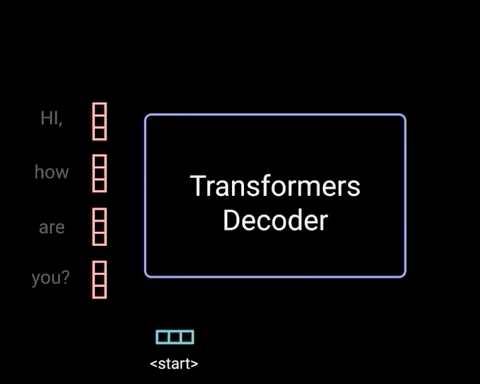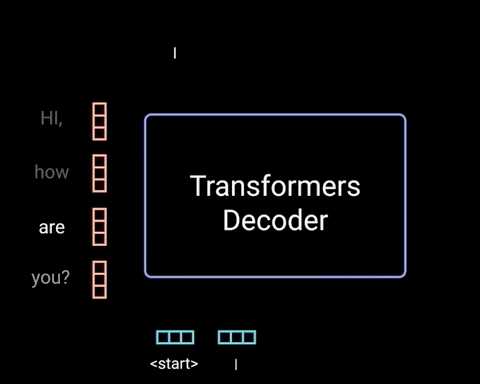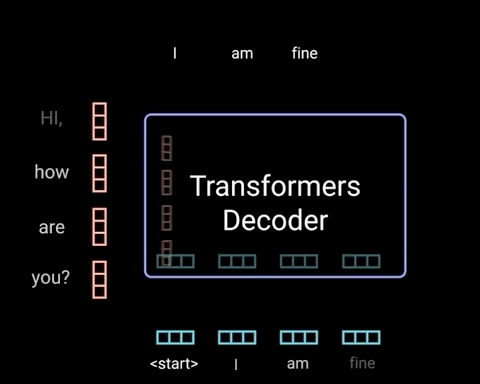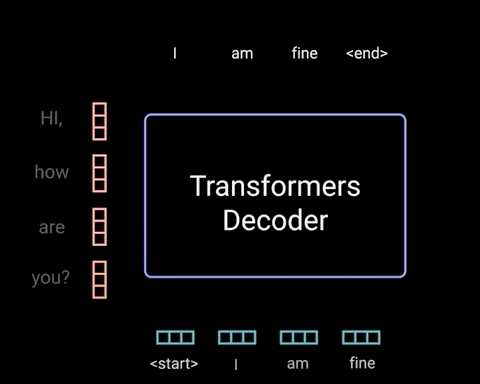
Diagram 1.8.2: an LLM performing a chatbot style task, to depict, with the Transformer as a black box, how newly generated tokens are fed as input back into the Transformer. Source: Illustrated Guide to Transformers Neural Network: A step by step explanation
